About Course
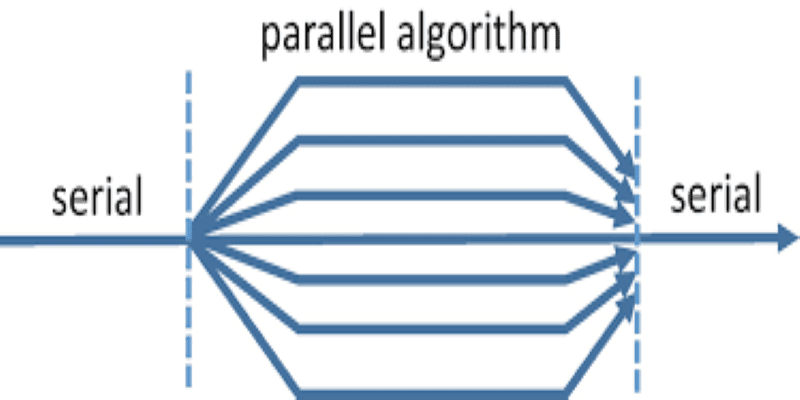
Parallel Algorithms. A conventional algorithm uses a single processing element. A parallel algorithm assumes that there are multiple processors.
These processors may communicate with each other using shared memory or an interconnection network. An algorithm designed for a large number (for example, a polynomial in the problem size) of processors can be simulated on a machine with a small number of a processor for a trade-off on time, and therefore is of practical value, while at the same time allowing us to test the limits of parallelism.
Many algorithmic design techniques in the parallel setting will be explored. Parallel complexity theory will also be briefly studied.
Course Content
Parallel Algorithms
-
Parallel Algorithms [Intro video]
00:00 -
Lec20: Analysis of Cole’s Merge Sort; Lower bound for sorting
00:00 -
Lec21: Sorting Lower bound; Connected Components
58:42 -
Lec 22: Connected Components (CREW)
00:00 -
Lec 23: Connected Components, Vertex Colouring
00:00 -
Lec 24: Sorting on a 2D mesh
00:00 -
Lec 25: Sorting on a 2D mesh
00:00 -
Lec 26: Sorting, Offline routing on a 2D mesh
00:00 -
Lec 27: Sorting on a 3D mesh
00:00 -
Lec 28: Mesh of Trees, Hypercube
00:00 -
Lec 29: Hypercube cont’d
00:00 -
Lec 30: Hypercube cont’d, butterfly network
00:00 -
Lec 31: Butterfly, CCC and Benes Networks
00:00 -
Lec 32: Butterfly, CCC and Benes Networks
00:00 -
Lec 33: Shuffle Exchange Graphs, de Bruijn Graphs
00:00 -
Lec 34: SEG, dBG (cont’d)
00:00 -
Lec 35: Circuit Value Problem is P-complete for NC-reductions
00:00 -
Lec 36: Ordered DFS is P-complete for NC-reductions
00:00 -
Lec19: Cole’s Merge Sort: Details
00:00 -
Lec 18: High level Description
00:00 -
Lec 1: Shared Memory Models – 1
00:00 -
Lec 2: Shared Memory Models – 2
00:00 -
Lec 3: Interconnection Networks
00:00 -
Lec 4: Cost and Optimality
00:00 -
Lec 5: Basic Techniques 1
00:00 -
Lec 6: Basic Techniques 2
00:00 -
Lec 7: Basic Techniques 3
00:00 -
Lec 8: Basic Techniques 4
01:03:58 -
Lec 9: Basic Techniques 5
53:54 -
Lec 10: Odd Even Merge Sort (OEMS)
00:00 -
Lec 11: OEMS, Bitonic-Sort-Merge Sort (BSMS)
00:00 -
Lec 12: BSMS, Optimal List Colouring
00:00 -
Lec 13: Description
00:00 -
Lec 14: Analysis
00:00 -
Lec 15: Applications
57:08 -
Lec 16: Applications
00:00 -
Lec 17: Fast optimal merge algorithm
00:00 -
Lec 37: Max Flow is P-complete for NC-reductions
00:00
Student Ratings & Reviews

No Review Yet
