About Course
Open RAN (O-RAN, ORAN) and Private 4G / 5G Networks: In this course, you will mainly learn two things:
1) Learn the Open RAN Concepts, Architectures, Interfaces, and the details related to them.
2) Learn how to build 4G & 5G networks using open-source Open RAN software and general-purpose, COTS hardware.
If you want to prepare yourself to build practical, and fully open telecom equipment, software programs, and end-to-end 4G/5G systems alternative and competitive to those produced by conventional Telecom companies, such as NOKIA, HUAWEI, SAMSUNG, ERICSSON, ZTE, etc., or want to learn how to build private 4G/5G networks, then this course is just for you. In this course, you will learn in detail most technical aspects of building end-to-end 4G and 5G systems including eNodeB/gNodeB, UE, and EPC/5GC.
Private networks, no matter who you ask (see: here, here, or here) have transitioned from lab toys to a multi-billion dollar industry. Open source too has left the lab and solutions from the likes of RedHat, OpenStack, O-RAN Alliance, and the Telecom Infra Project are a growing presence in operators’ networks globally. As the footprint of open source grows, and network operators see the benefits of deploying open-source, the industry is responding by developing open source solutions moving up the stack. Now with the introduction of the Magma project, open-source is moving into complex network functions like the core of the 4G and 5G mobile networks.
Dumping gas on the open and private network fire, the FCC has made available commercially deployable CBRS spectrum that we see taking off in the recent auction and as Spectrum Access Systems (SASs) go live. With its 3-tier access, CBRS means anyone can get a meaningful chunk of airwaves with 25 times (or more) the power of most Wi-Fi networks to deliver high-quality wireless services.
In light of these changes, in this version of the build your own network how-to, I will move our target from a lab network to a commercial-grade LTE network deployment. Let’s get started.
After you complete watching all the lecture videos of the course, you will get a professional certificate of completion.
=============
Open RAN and Private 5G Networks
The content of the course is listed below.
- What is Open RAN and why do we need it?
- Understanding Classical and Distributed RAN (D-RAN)
- Equipment from traditional vendors (BBU & Boards)
- C-RAN or Centralised RAN)
- V-RAN or Virtualizes RAN
- Evolution towards Open RAN
- Open RAN Groups & Initiatives
- Telecom Infra Project
- ORAN Alliance
- Open Ran players & Ecosystem
- Open Ran Trials & deployments
- RU/CU/DU Split
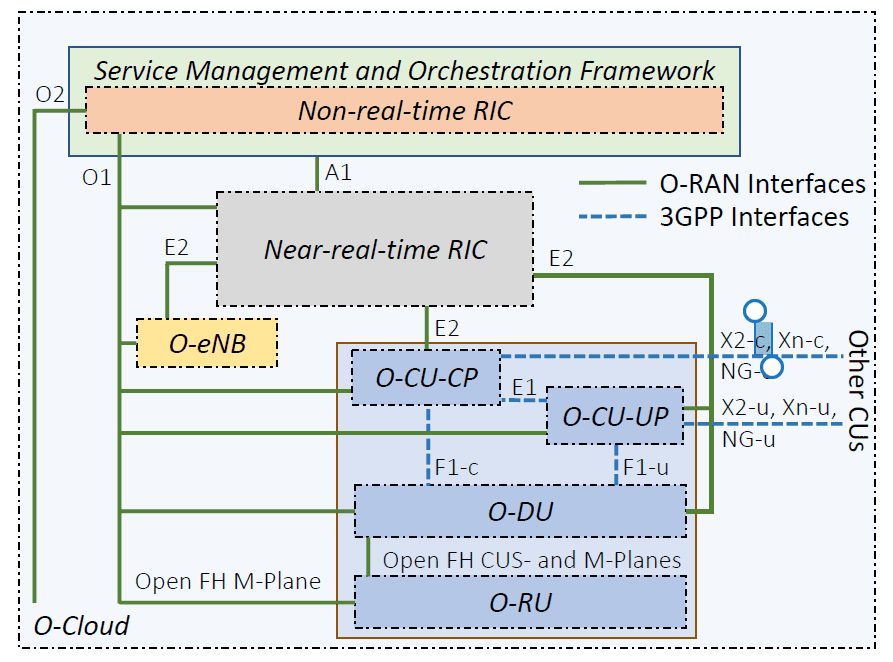
- Oran Architecture
- Service Management and Orchestration Framework (SMO)
- RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC)
- xAPPs, rAPPs, AI, ML
- O-Cloud, O-CU, O-DU, O-RU
- Relevant interfaces in O-RAN architecture
- Different RAN split options
- Which Option split to consider
- Relevant interfaces in O-RAN architecture
- Security issues.
- Different companies with different cases
- Real-live examples using O-RAN
- Relevant success stories
- Recommendations and suggestions
If you want to prepare yourself to build practical, and fully open telecom equipment, software programs, and end-to-end 4G/5G systems alternative and competitive to those produced by conventional Telecom companies, such as NOKIA, HUAWEI, SAMSUNG, ERICSSON, ZTE, etc., or want to learn how to build private 4G/5G networks, then this course is just for you. In this course, you will learn in detail most technical aspects of building end-to-end 4G and 5G systems including eNodeB/gNodeB, UE, and EPC/5GC.
After you complete watching all the lecture videos of the course, you will be able to get a professional certificate of completion.
============
Private networks, no matter who you ask (see: here, here, or here) have transitioned from lab toys to a multi-billion dollar industry. Open source too has left the lab and solutions from the likes of RedHat, OpenStack, O-RAN Alliance, and the Telecom Infra Project are a growing presence in operators’ networks globally. As the footprint of open source grows, and network operators see the benefits of deploying open source, the industry is responding by developing open source solutions moving up the stack. Now with the introduction of the Magma project, open-source is moving into complex network functions like the core of the 4G and 5G mobile networks.
Dumping gas on the open and private network fire, the FCC has made available commercially deployable CBRS spectrum that we see taking off in the recent auction and as Spectrum Access Systems (SASs) go live. With its 3-tier access, CBRS means anyone can get a meaningful chunk of airwaves with 25 times (or more) the power of most Wi-Fi networks to deliver high-quality wireless services.
In light of these changes, in this version of the build your own network how-to, I will move our target from a lab network to a commercial-grade LTE network deployment. Let’s get started.
The Ingredients
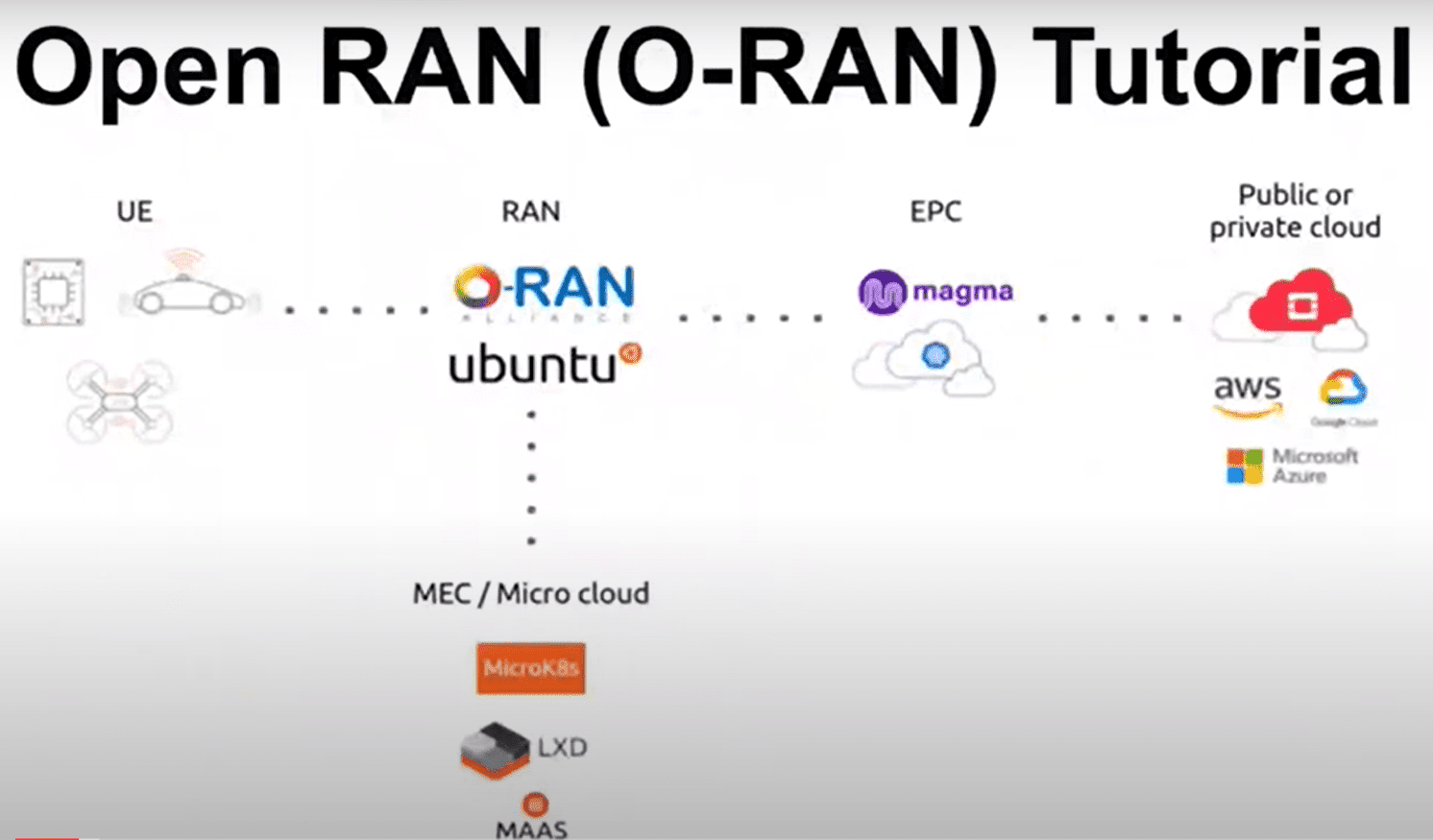
There are 6 key components to an open and private LTE network:

Course Content
Introduction to the course of SDR
-
About the Instructor Dr. Jehad Hamamreh
03:09 -
Motivation and Course Content – Part 1
34:36 -
Motivation and Course Content – WHY, WHAT and HOW – Part 2
46:41 -
02:19
