About Course
Gasdynamics: Fundamentals and Applications.
In the previous century, humanity quickly moved from enabling mechanical flight to flying farther, higher, and faster. Now, humanity is endeavoring to explore and colonize other planets. Similarly, engineers are seeking to make compact and efficient systems in the domains of energy and power.
All these scenarios and several more, including natural events like explosive volcanic eruptions, involve the high-speed Flow of gases. Speeds at which the compressible nature of gases becomes significant. In this course on the fundamentals and applications of gas dynamics, we shall understand and model the compressible flow phenomena of gases from the first principles.
in this Gasdynamics course, We will discover the importance of Mach number (M), the ratio of the flow velocity to the speed of sound, in describing such flows. We will find a close coupling of thermodynamics and fluid dynamics. We shall encounter and explain counter-intuitive behavior as the flow Mach number changes from subsonic (M<1) to supersonic (M>1). These are wave-dominated flows.
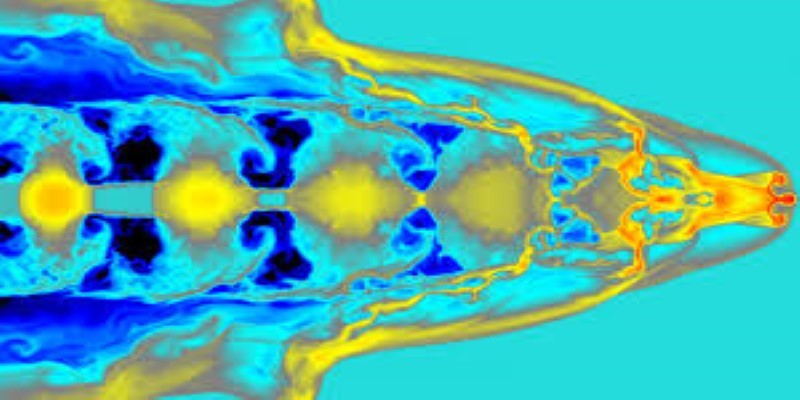
The shock wave is a particularly exciting phenomenon existing only in supersonic flows. We will learn about shock waves and their interactions, and means of producing them in a controlled manner in the laboratory.
The understanding of gas dynamics gained will be applied to design and analyze typical engineering systems like nozzles, diffusers, intakes, shock tubes, wind tunnels, pipe flows, to name a few.
Flow visualizations taken in the unique high-speed experimental facilities at the Indian Institute of Science will enable deeper insights. Special topics on hypersonic flows and shock wave boundary layer interactions will be introduced towards the end of this Gasdynamics course.
This Gasdynamics course is an elective course suitable at advanced undergraduate or postgraduate levels. Participants must have undergone a basic course in fluid dynamics and thermodynamics and must be familiar with the solution of ordinary differential equations and partial differential equations.
Course Content
Gasdynamics: Fundamentals and Applications
-
lec60 Concluding Remarks
00:00 -
lec43 1D flow with friction- Fanno flow- III
00:00 -
lec42 1D flow with friction- Fanno flow- II
00:00 -
lec41 1D flow with friction- Fanno flow- I
00:00 -
lec40 Varying area flow – Numericals- IV
00:00 -
lec39 Varying area flow – Numericals- III
00:00 -
lec38 Varying area flow – Numericals- II
00:00 -
lec37 Experimental facilities
00:00 -
lec36 Diffusers Intakes/Inlets
00:00 -
lec35 Varying area flow- Numericals- I
00:00 -
lec34 Converging & Diverging Nozzle Operation
00:00 -
lec33 Converging Nozzle and Chocking
00:00 -
lec32 Varying Area Duct Flows-II
00:00 -
lec31 Varying Area Duct Flows- I
00:00 -
lec44 1D flow with friction- Fanno flow – Numericals
00:00 -
lec45 1D Flows with Heat Addition: Rayleigh Flows- I
00:00 -
lec46 1D Flows with Heat Addition: Rayleigh Flows- II
00:00 -
lec59 Shock Boundary Layer Interaction- II
00:00 -
lec58 Shock Boundary Layer Interaction- I
00:00 -
lec57 Edney Shock Interaction
00:00 -
lec56 Hypersonic Flows – II
00:00 -
lec55 Hypersonic Flows – I
00:00 -
lec54 Method of Characteristics- Applications
00:00 -
lec53 Method of Characteristics: 2D Supersonic Flow -II
00:00 -
lec52 Method of Characteristics: 2D Supersonic Flow – I
00:00 -
lec51 Small perturbation theory- III
00:00 -
lec50 Small perturbation theory- II
00:00 -
lec49 Small perturbation theory- I
00:00 -
lec48 Generalized 1D Flows
00:00 -
lec47 1D Flows with Heat Addition: Rayleigh Flows – Numericals
00:00 -
lec30 Oblique Shock and Expansion waves – Numerical
00:00 -
lec29 Shock Reflection
00:00 -
lec28 Shock Expansion Method
00:00 -
lec13 Sonic/ Star properties
00:00 -
lec12 Pitot tube
00:00 -
lec11 Stagnation properties
00:00 -
lec10 Speed of Sound- Numerical
00:00 -
lec09 Speed of Sound
00:00 -
lec08 Quasi-1D Assumption
00:00 -
lec07 Flow equations – Differential Form
00:00 -
lec06 Flow equations – Integral Form
00:00 -
lec05 Thermodynamics – Numerical
00:00 -
lec04 Thermodynamics – 02
00:00 -
lec03 Thermodynamics – 01
00:00 -
lec02 Flow Regimes
00:00 -
lec01 Introduction
00:00 -
lec14 Numerical
00:00 -
lec15 Normal Shock – I
00:00 -
lec16 Normal Shock – II a
00:00 -
lec27 Expansion waves
00:00 -
lec26 Oblique Shock Waves
00:00 -
lec25 Unsteady Flows- Numerical
00:00 -
lec24 Shock Tube Relations
00:00 -
lec23 Waves of finite amplitude
00:00 -
lec22 Waves of infinitesimal Amplitude
00:00 -
lec21 The Shock Tube
00:00 -
lec20 Normal Shocks – Numerical
00:00 -
lec21 The Shock Tube
00:00 -
lec20 Normal Shocks – Numerical
00:00 -
lec19 Normal Shock- IV
00:00 -
lec18 Normal Shock- III
00:00 -
lec17 Normal Shock – II b
00:00 -
Intro – Gasdynamics: Fundamentals and Applications
00:00
Student Ratings & Reviews

