Description
This is the full Matlab Simulation Codes package, which is used to generate the results presented in the paper titled “Multi-cell, Multi-user, and Multi-carrier Secure Communication Using Non-Orthogonal Signals’ Superposition with Dual-Transmission for IoT in 6G and Beyond”.
====== Work Summary =====
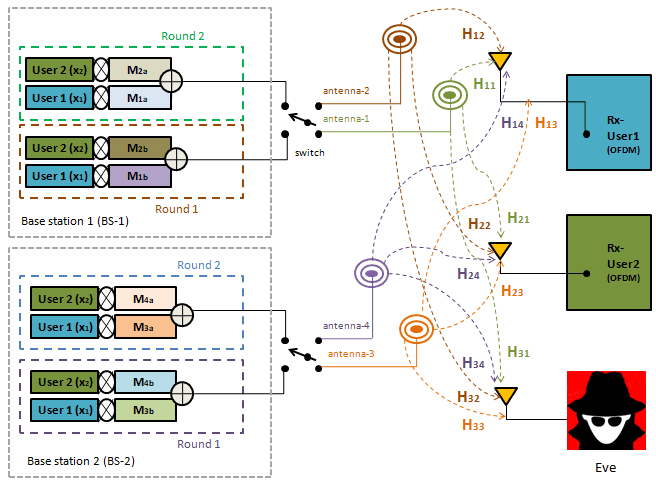
Considering the advancements of the internet of things (IoT) in 6G and beyond communications, data transmission security in IoT devices has received extensive interest because of their significant features, such as low computational complexity, led by low power requirements. In such devices, the conventional cryptographic techniques may fail to provide secure communication. To fight this drawback, physical layer security (PLS) has remarkable potential to provide security solutions suitable for such applications. In this work, a highly effective PLS technique is proposed for providing secure communication against external and internal eavesdroppers in a downlink multi-carrier IoT communication system. In our proposed system, we considered two base stations, where each base station consists of a transmitter with a single active antenna that is trying to communicate with two single antenna IoT devices/users in the presence of a passive eavesdropper. In the proposed algorithm, frequency selective channel-based pre-coder matrices and the dual transmission approach are jointly employed. The dual-transmission is performed simultaneously from two base stations to provide security against internal and external eavesdroppers. The proposed system is suitable for IoT based applications. Also, the potential capabilities of our proposed algorithm are proved by extensive mathematical and simulation analysis.