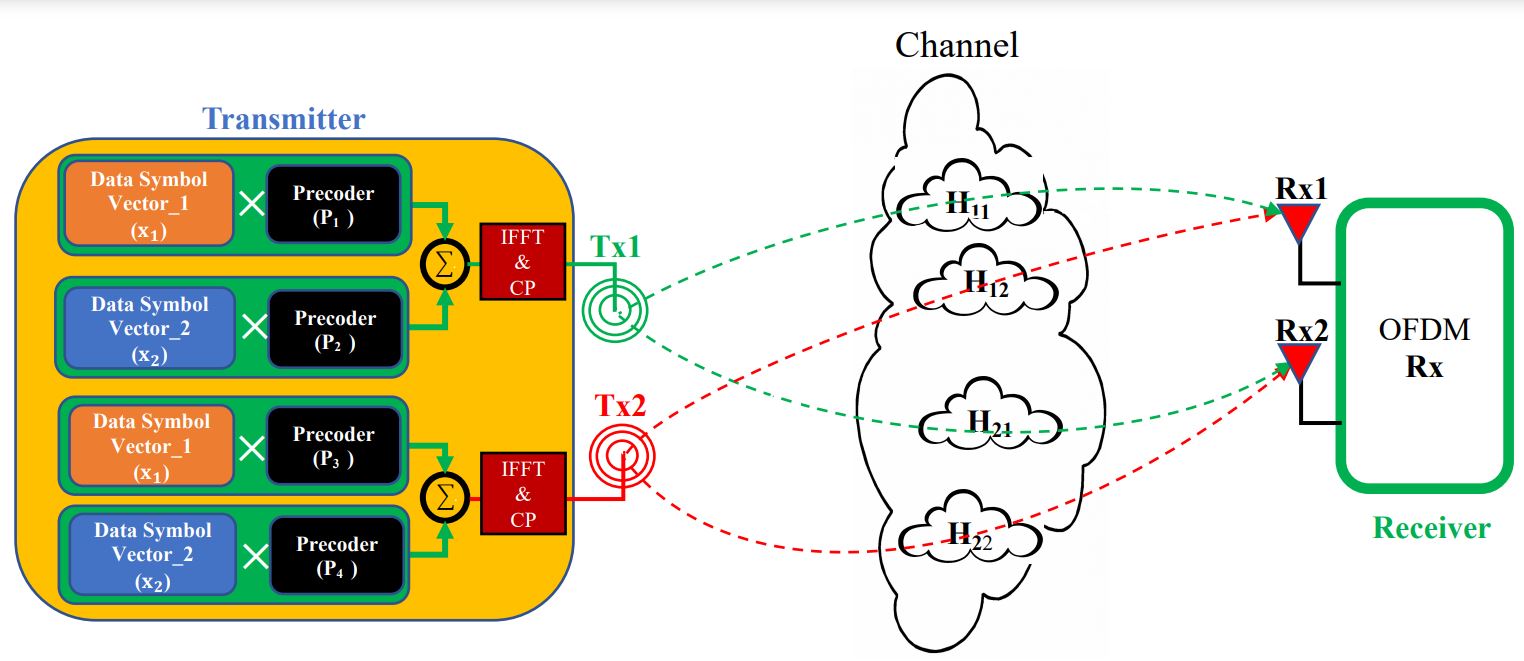
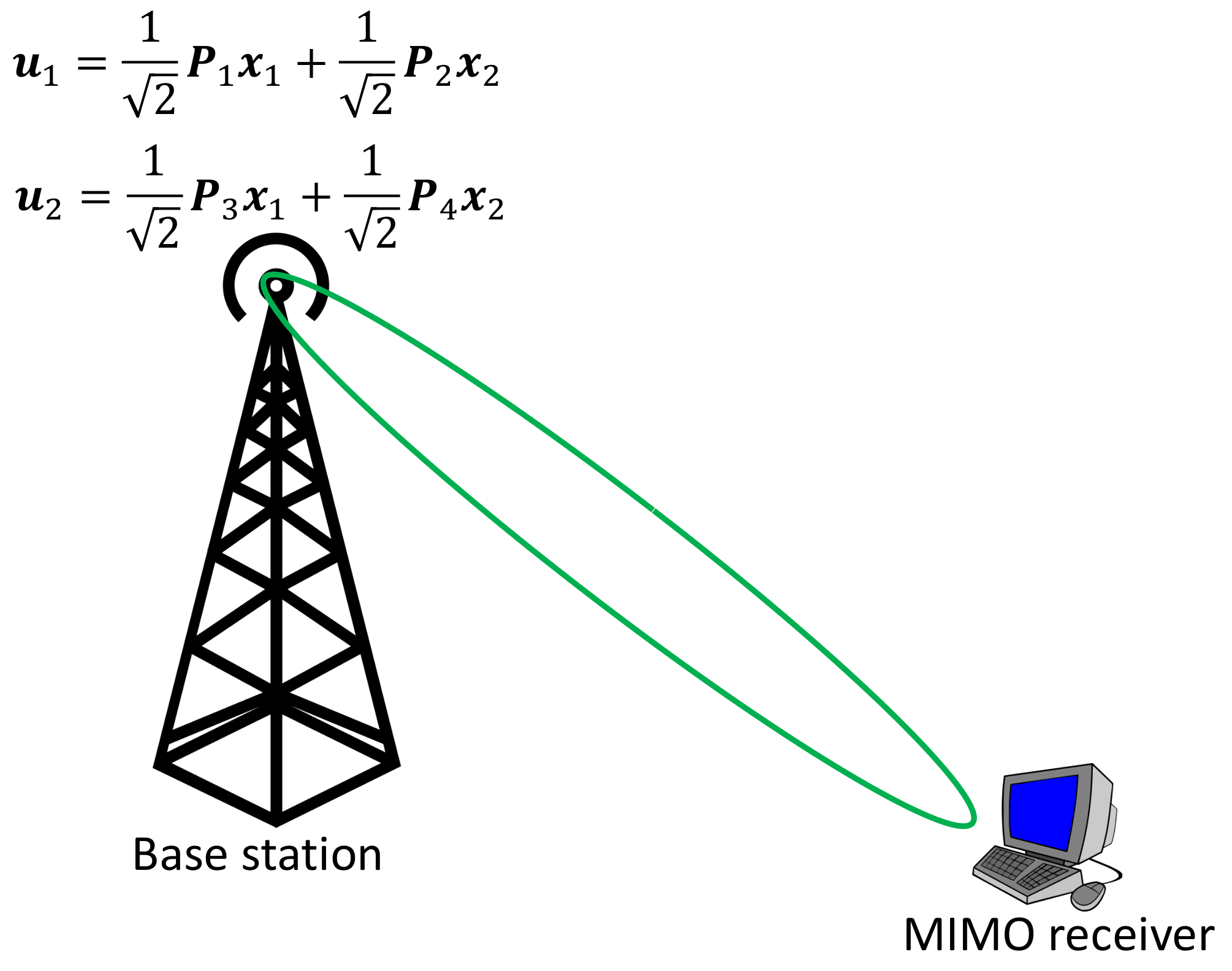
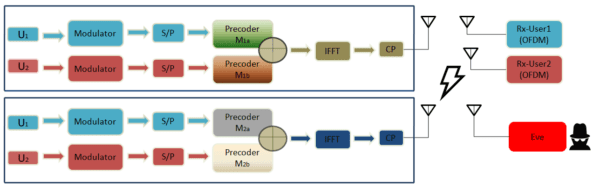
Description
You will get the files that contain all the codes for all the figures in the paper titled “Hybrid MIMO: A New Transmission Method For Simultaneously Achieving Spatial Multiplexing and Diversity Gains in MIMO Systems“, which can be found at https://doi.org/10.46470/03d8ffbd.549d270b
============ Summary ==========
Multiple input multiple-output (MIMO) technology has evolved over the past few years into a technology with great potential to drive the direction of future wireless communications. MIMO technology has become a solid reality when massive MIMO systems (MIMO with a large number of antennas and transceivers) were commercially deployed in several countries across the world in the recent past. Moreover, MIMO has been integrated into state-of-the-art paradigms such as fifth-generation (5G) networks as one of the main enabling technologies. MIMO possesses many attractive and highly desirable properties such as spatial multiplexing, diversity gains, and adaptive beamforming gains that leads to high data rates, enhanced reliability, and other enhancements. Nevertheless, beyond 5G technologies demand wireless communication systems with, among other properties, immensely higher data rates and better reliability simultaneously at the same time. In this work, a new, novel MIMO technique for simultaneously achieving multiplexing and diversity gains as well as completely eliminating any processing at the MIMO receiver, leading to advantages such as low complexity and low power consumption, is proposed. The proposed technique employs the design of interference-canceling matrices, which are calculated from the channels between the transceiver antennas, where the matrices are employed at the base station to help achieve multiplexing and diversity gains simultaneously. The novelty and efficiency of the introduced paradigm is demonstrated via mathematical models and validated by Monte Carlo simulations. Results indicate that the proposed system outperforms conventional MIMO models.
======= Preface ================
Multiple input multiple-output (MIMO) technology has
highly desirable properties such as high throughput and
high spectral efficiency, which is enabled by its spatial
multiplexing mode; and better reliability, which is enabled
by its diversity mode [1] [2]. It has evolved from a mere
research concept to a real-world technology and has been
integrated into state-of-the-art wireless network standards
such as IEEE 802.11n, 3GPP long-term evolution (LTE),
mobile WiMAX systems, LTE-Advanced (E-UTRA), and
recently in 5G systems. Due to the exponential increase in
the number of connected things, the ability of MIMO to have
high user capacity is a key requirement for the current 5G-IoT
era and beyond technologies (6G). MIMO has the ability
to provide enhanced throughput even under conditions of
interference, signal fading, and multipath. The demand for
wireless communication services is continuously increasing
as a consequence of the massive spread of wireless devices
featured by high mobility and ease of use. Additionally, the
surge in wireless data communication is primarily driven
by the huge number of beneficial applications customized
for mobile users. For instance, the Internet of things (IoT)
is a network of millions of interconnected wireless devices
accessible through the internet. The idea of IoT was made
possible by advanced wireless communication technologies
(5G and beyond). This is due to the many advantages such
as increased data rate, reduced delay, and enhanced cellular
coverage in the communication technologies over preceding
technologies. These advantages will have a huge impact on
future intelligent service delivery. Some areas influenced
by IoT are autonomous driving, healthcare, entertainment,
industrial appliances, smart cities, smart energy grids, sports,
remote surgery, and drone delivery applications. Moreover,
countries around the world are employing IoT technologies
to combat challenges such as traffic congestion, insecurity,
and infrastructure management caused by overpopulation.
MIMO systems are used in IoT networks to increase data rate
and diversity. Therefore, MIMO has set its self as one of the
leading technology that will continue to shape the future of
wireless communications