About Course
Strategies for Sustainable Design
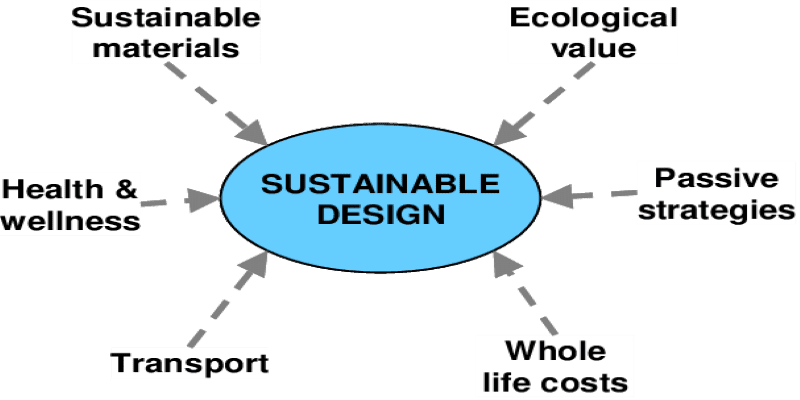
Sustainable design is the practice of creating and maintaining systems that are ecologically sound, resource efficient, and cost-effective. It is an important part of creating a better and more sustainable future. The goal of sustainable design is to reduce our environmental footprint while still providing the benefits of modern life. The first step to sustainable design is to understand the environmental, economic, and social impacts of our actions. This means assessing the resources needed to produce a product or service and considering the full life cycle of the product, from production to disposal. This assessment should include the impacts of energy use, water use, waste streams, and other environmental considerations. The next step is to reduce the environmental impact of the product or service. This can be done through energy efficiency, resource conservation, and use of renewable energy. Strategies for energy efficiency include using natural lighting, building materials with high insulation values, and using energy efficient appliances. Resource conservation can be achieved through the use of recycled materials, reusing materials, and designing durable and long-lasting products. Renewable energy sources can be used to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. Once the environmental impact of the product or service has been reduced, the next step is to look at the economic costs. This means considering the cost of production, the cost of materials, and the cost of maintenance. The goal is to create products that are cost-effective and use renewable, energy-efficient resources. Finally, the social impacts of the product or service should be considered. This includes the impact on local communities, the health and safety of people, and the impact on the environment. Sustainable design should strive to create products and services that meet the needs of people and communities, while also considering the environment. Sustainable design is a complex process and requires a thoughtful approach. By understanding the environmental, economic, and social impacts of our actions, we can create products and services that are resource efficient, cost-effective, and beneficial to both people and the environment.
The course discusses sustainability principles and concepts from across various domains. Elaborates on sustainability definitions, aspects, dynamic nature of it, and its application in everyday life. Further, it discusses global efforts from UNFCCC, IPCC, and other agencies for developing context-based solutions and climate change mitigation efforts. Involves field visits, real-life case examples, and assignments. Includes study on building technologies to improve efficiency and response to surroundings.
Focuses on basic scientific principles underlying the environmental performance of the built environment and designing for efficacy on EIA/LCA. It elaborates about NBC of India, CNBC, and SA Methods also such as GRIHA, LeNS tools, etc. Overall, it touches on UN SDG and systemic analysis for an easy understanding of assessment for students. The course provides a state of the art study material using the latest research papers, journals, books, and reports, etc.
Strategies for Sustainable Design course layout
Week 1: Definitions and Perspectives on Sustainability in Industrial Design and Built Environments
Week 2: ESE Aspects of Sustainability and Climate Change Mitigation
Week 3: Current National and International Scenario of SD and Dependence on Energy
Week 4: Impact of Pollutions and Design Processes with Alternative Solutions for Health of Ecosystem
Week 5: Environmental Impact Assessment and Lifecycle Analysis
Week 6: Policy, Growth, Development and 3R’s for Consumption
Week 7: NBC, ECBC, and SA Methods such as GRIHA
Week 8: UN SDG and System Design tools such as SPSS, MSDS by LeNS
Week 9: Vernacular and Responsive Design using Net-Zero Energy, Lighting, Ventilation, Views, etc., for Human Comfort
Week 10:Design for Sustainability and Nature as Inspiration
Week 11: International Conventions, Laws and Emerging Technologies for SD
Week 12:SD Case Studies and Summary
Join to Strategies for Sustainable Design course
Course Content
Strategies for Sustainable Design
-
Strategies for Sustainable Design _ Course Introduction
05:12 -
Strategies for Sustainable Design – Welcome Lecture
53:01 -
Various Perspectives around Sustainability
37:34 -
Spheres of Energy Efficient/Green/Environmental/Sustainable Designs
01:01:08 -
Environmental Sustainability
31:01 -
Social Sustainability
28:59 -
Economic Sustainabilty
14:11 -
Climate Change Mitigation and the Way Forward
33:47 -
Future of Human Habitation Design
29:13 -
Relevance of Sustainable Design in Contemporary Context
31:28 -
Built Environment and Energy Consumption
33:12 -
Reliance and Dependence of Building Design on Energy
34:37 -
Current Scenario of Sustainable Design: Indian
29:45 -
Current Scenario of Sustainable Design: International
22:10 -
Designing Strategically for Preventing pollution: Air, Water, Soil, Noise, Light Radiation, etc
40:18 -
Low Environmental Impact
32:25 -
Thinking for Alternatives through Systemic Design
17:27 -
Consumption and Consumerist Lifestyle
23:34 -
Environmental impact Assessment
31:20 -
Lifecycle Analysis Part A
35:39 -
Lifecycle Analysis Part B
39:08 -
Growth and Development in Construction and Allied Sectors
16:35 -
Policy Push in Real Estate and Manufacturing Sectors
23:49 -
Policy Push for Development of the Low Economic Regions
14:15 -
Sustainable Building Materials
38:10 -
Reduce/Reuse/Recycle
27:35 -
National Building Code 2016 – Part 11 and Energy Conservation Building Code
37:46 -
Guidelines for Building Design by SA Methods: GRIHA
55:56 -
UN SDG for Sustainable Development
52:08 -
LeNS Design Method and Tools such as SPSS, MSDS, DE
01:34:22 -
Vernacular Design Case Example
53:08 -
Climate Responsiveness
42:17 -
Thinking the Unthinkable: Need for Innovation in Design Process
52:22 -
Design for Net-Zero Energy, Lighting, Ventilation, Views and Human Comfort
01:08:00 -
D4S with Inspiration from Nature
52:21 -
D4S for Optimization of Manufacturing
35:50
