About Course
Electrochemical impedance Spectroscopy
This course will introduce the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy technique and illustrate its use to characterize electrochemical processes. Details regarding the correct method of data acquisition and analysis, along with pitfalls to watch out for, will be discussed.
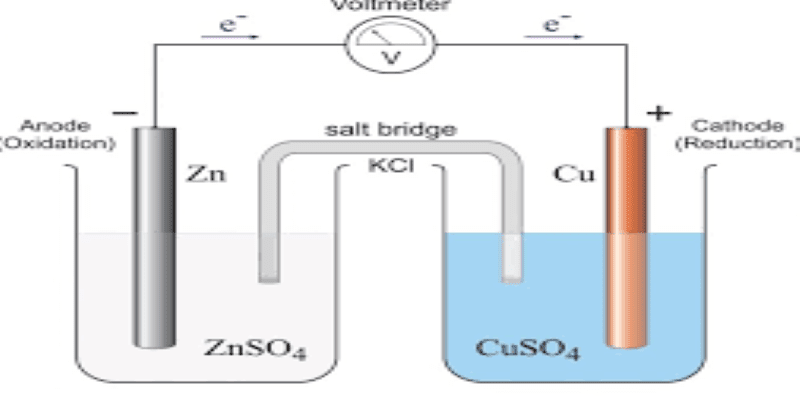
Week 1: Introduction to electrochemistry, electrode-electrolyte interface, reference electrode, three-electrode cell, supporting electrolyte, the rate constant, EIS basics, electrical elements, differential impedance, time-domain results, graphical representation of impedance data in Bode and Complex plane plots, other techniques.
Week 2: Experimental details: Instrumentation, single and multi-sine inputs, FFT details, frequency range and resolution, cross-correlation, multi sine: odd harmonics and non-harmonic choices, crest factor, spectral leakage, windowing
Week 3: Data validation: Kramers Kronig Transforms (KKT), Linearity, causality, stability, impedance vs. admittance, applications, and limitations, Alternatives – measurement model analysis and linear KKT
Week 4: Data analysis: Electrical Equivalent Circuits, choice of circuits, confidence intervals, AIC, initial values, distinguishability, zeros and poles representation, charge transfer resistance and polarization resistance, Maxwell, Ladder, and Voigt circuits
Week 5: Reaction mechanism analysis, linearization of governing equations, derivation of impedance expression for a simple electron transfer reaction; two-step reactions with one adsorbed intermediate
Week 6: Reaction mechanism analysis (continued), development of impedance expression for multiple reactions, an example reaction exhibiting negative resistance, an example three-step reaction with 2 adsorbed intermediates
Week 7: Reaction mechanism analysis (continued), development of impedance expression for a catalytic reaction exhibiting negative resistance, reactions with Frumkin isotherm practical challenges in the extraction of kinetic information, list of various patterns of complex plane plots reported in the literature
Week 8: Diffusion effects, Warburg Impedance, finite and semi-infinite cases, effect of change in dc potential, and boundary layer thickness.
Week 9: Constant phase elements (CPE), porous electrodes
Week 10: Passivation and film formation, point defect model (PDM), and extensions. Description of a few selected applications of EIS: Corrosion, biosensors, fuel cells, mechanistic analysis
Week 11: Nonlinear EIS (NLEIS), introduction, mathematical background (Taylor series, Fourier series, modified Bessel functions), NLEIS for a simple electron transfer reaction, reaction with adsorbed intermediates, Nonlinear charge transfer, and polarization resistances
Week 12: Effect of instabilities in traditional EIS- calculation using NLEIS methodology, solution resistance effects, Detection of nonlinearities using KKT, NLEIS with Frumkin and Temkin isotherm, evaluation of related technique: electrochemical frequency modulation (EFM)
Join now!
Course Content
Electrochemical impedance Spectroscopy
-
Answers to Assignments – 05 TO 08
00:00 -
Multi sine, odd harmonic, non-harmonics, crest factor, spectral leakage
00:00 -
FFT details, frequency range and resolution, cross correlation
00:00 -
Type of analyzers, single and multi sine
00:00 -
Assignment 02
00:00 -
Linear KKT illustration
00:00 -
Linearity, causality, stability, impedance vs. admittance, measurement model
00:00 -
Introduction to KKT
00:00 -
Assignment 03
00:00 -
Introduction to EEC, Choice of circuits, confidence intervals, AIC
00:00 -
EEC fitting, initial values, distinguishability
00:00 -
Zero/pole representation, Rt and Rp
00:00 -
Maxwell, Voigt, Ladder circuits, choice of initial values illustrated
00:00 -
Windowing
00:00 -
NLEIS. Introduction and mathematical background
00:00 -
Answers to Assignments – 01 TO 04
00:00 -
Application – other techniques HA, EFM
00:00 -
NLEIS Experimental aspects. FFT, PSD, THD
00:00 -
Frumkin and Temkin isotherms
00:00 -
Detection on nonlinearities using KKT
00:00 -
Solution resistance effects
00:00 -
Instabilities
00:00 -
Galvanostatic simulations
00:00 -
Rt and Rp estimation
00:00 -
Two step reaction (continued)
00:00 -
Two step reaction
00:00 -
Electron Transfer reaction
00:00 -
Assignment 04
00:00 -
Three step reaction with two adsorbed intermediates
00:00 -
Applications
00:00 -
PDM
00:00 -
Films, PDM
00:00 -
Porous electrodes
00:00 -
CPE
00:00 -
Assignment 01
00:00 -
Introduction to other techniques
00:00 -
Graphical representation of data (Complex plane, Bode)
00:00 -
Time domain results
00:00 -
Rate constant, concept of impedance, Z of electrical elements, differential impedance
00:00 -
Electrochemistry, double layer, 3 electrode systems, supporting electrolyte
00:00 -
Detailed Syllabus
00:00 -
Warburg
00:00 -
Warburg
00:00 -
E-EAR reaction, negative resistance (2 of 2)
00:00 -
E-EAR reaction, negative resistance (1 of 2)
00:00 -
Examples with Frumkin or Temkin isotherms
00:00 -
Two step reaction with an intermediate (3 of 3)
00:00 -
Two step reaction with an intermediate (2 of 3)
00:00 -
Two step reaction with an intermediate (1 of 3)
00:00 -
Simple electron transfer reaction
00:00 -
Catalytic mechanism.
00:00 -
Challenges in RMA
00:00 -
Patterns reported in experiments
00:00 -
Bounded Warburg
00:00 -
Warburg
00:00 -
Introduction to Electrochemical impedance Spectroscopy
00:00
Student Ratings & Reviews

